In the field of telecommunications, radio waves play a crucial role in wireless information transmission. Among the various frequency bands used, Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) are two of the most significant. This article delves into the fundamental aspects and characteristics of these bands, examining their benefits, limitations, and practical uses.
What is VHF?
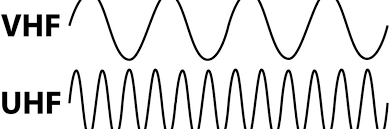
Very High Frequency, or VHF, encompasses a specific range of radio frequencies that serve multiple communication purposes, from broadcasting to navigation systems. These signals operate within wavelengths of 1 to 10 meters, with frequencies spanning from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz). Compared to UHF waves, VHF signals can traverse greater distances, making them particularly valuable for applications requiring extensive coverage areas, such as aviation communication, marine operations, and broadcast television.
VHF waves find extensive applications across various sectors. Key applications include:
- Two-way Radio Communication: Emergency response teams, law enforcement agencies, and fire departments rely heavily on VHF frequencies for their communication needs. The maritime industry also utilizes VHF radio systems for vessel-to-vessel and vessel-to-shore communications.
- Television Broadcasting: Historically, VHF bands were the primary medium for analog television transmission before digital TV emerged. Channels 2 through 13 (54-216 MHz) were commonly designated for television broadcasting globally.
- Air Traffic Control: The aviation industry depends on VHF radio systems for reliable communication between ground controllers, flight crews, and support staff. These frequencies ensure dependable long-range communication essential for aviation safety.
- FM Radio Broadcasting: Commercial FM radio stations utilize VHF band frequencies to deliver high-fidelity audio content. Most FM receivers operate within the 88-108 MHz frequency range.
What are the advantages of using VHF frequencies over UHF frequencies?
Several distinct benefits make VHF frequencies preferable to UHF frequencies in certain scenarios:
Longer Range: VHF waves possess extended wavelengths in comparison to UHF waves, enabling them to cover greater distances with minimal signal degradation. This characteristic makes VHF particularly advantageous for applications requiring extensive coverage areas, such as maritime communications and aviation control systems.
Better Penetration: VHF frequencies demonstrate superior penetration capabilities through physical barriers such as buildings and vegetation when compared to UHF waves. This inherent property makes VHF frequencies the preferred choice for maintaining reliable communication in urban environments and heavily wooded areas.
Less Susceptible to Interference: The VHF spectrum typically experiences less congestion than UHF frequencies, resulting in reduced competition for bandwidth allocation. This translates to minimal interference and enhanced communication clarity, particularly in densely populated regions or areas with high radio frequency utilization.
Efficient Antenna Design: VHF systems utilize more compact and shorter antennas compared to their UHF counterparts, facilitating easier installation and reducing vulnerability to wind effects. This advantage proves particularly beneficial in applications where antenna dimensions and mass are crucial factors, such as portable communication devices and handheld radios.
Cost-Efficiency: VHF systems generally offer more economical solutions compared to UHF alternatives, primarily due to their longer wavelength characteristics. These systems typically require fewer infrastructure components like base stations or signal repeaters to achieve comparable coverage, resulting in reduced installation and maintenance expenses.
What about UHF?
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) encompasses electromagnetic waves ranging from 300 megahertz (MHz) to 3 gigahertz (GHz). UHF technology is widely employed in communication systems, offering benefits such as reduced wavelengths, which enables the use of compact antennas and enhanced signal penetration through various obstacles. UHF radio systems find extensive applications across multiple sectors, including broadcasting, bidirectional communication networks, wireless data transmission, and numerous other applications.
Common applications where UHF frequencies are preferred over VHF frequencies:
UHF frequencies demonstrate superiority over VHF in various scenarios due to their distinct characteristics. Several notable applications where UHF frequencies are the preferred choice include:
Two-Way Radio: UHF frequencies excel in two-way radio communications, particularly in environments requiring short to medium-range transmissions. These frequencies prove invaluable in settings such as warehouse facilities, construction projects, and security operations within buildings or enclosed complexes, where clear and reliable communication is essential.
Wireless Microphones and Audio Systems: The UHF spectrum stands out as the preferred choice for wireless microphone implementations, owing to its superior capability to transmit high-fidelity audio signals with minimal interference. The abundance of available channels within the UHF range enables multiple devices to operate simultaneously, significantly reducing the risk of cross-device interference and ensuring optimal performance.
RFID Technology: UHF frequencies play a pivotal role in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems, offering enhanced capabilities compared to other frequency ranges. These frequencies enable RFID tags and readers to achieve superior data transfer speeds and extended read ranges, making them particularly effective for applications such as inventory tracking, supply chain monitoring, and sophisticated access control systems.
Satellite Communication: In the realm of satellite communications, UHF frequencies demonstrate exceptional utility, especially in low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite operations. The characteristics of UHF signals allow for efficient transmission and reception using compact, energy-efficient antenna systems, making them ideally suited for various satellite communication applications.
Remote Control Systems: UHF frequencies have become the standard in remote control applications, powering everything from drone operations to model aircraft and remote-operated vehicles. The extended transmission range offered by UHF signals ensures precise control and superior navigation capabilities for these devices.
How do UHF frequencies compare to VHF frequencies in terms of signal quality and interference resistance?
UHF and VHF frequencies exhibit distinct characteristics regarding signal quality and interference resistance.
Signal Quality:
UHF frequencies face greater challenges in maintaining signal quality compared to their VHF counterparts. Their shorter wavelengths make them more vulnerable to signal attenuation, particularly in urban environments with numerous obstacles. These frequencies experience greater absorption and reflection by structural elements, potentially leading to diminished signal strength and quality degradation.
Conversely, VHF frequencies demonstrate superior signal quality characteristics, particularly in terms of coverage range and obstacle penetration. Their longer wavelengths facilitate better propagation through various barriers, including buildings and vegetation, resulting in more consistent and reliable signal reception. VHF signals show greater resilience to environmental factors that typically cause signal deterioration.
Interference Resistance:
When it comes to interference resistance, UHF frequencies hold a distinct advantage. The UHF spectrum generally experiences less congestion, offering more channel availability with reduced spectrum interference. This translates to clearer communication channels with minimal signal overlap and enhanced reliability.
VHF frequencies, operating at lower frequencies, tend to be more susceptible to interference from various radio sources. The VHF spectrum often experiences higher congestion levels, particularly in urban areas with numerous devices utilizing these frequencies. This congestion can result in increased signal interference, potential transmission conflicts, and reduced overall system effectiveness.
When choosing between UHF and VHF frequencies for specific applications, careful consideration of multiple variables is essential. The decision-making process should account for environmental conditions, distance requirements, and the presence of potential interference sources.
To clarify the distinction, VHF encompasses radio frequencies within the 30 to 300 MHz range, primarily utilized for communication, broadcasting, and navigational systems. In contrast, UHF spans frequencies from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, offering different operational characteristics.
These frequency bands possess unique attributes and operational benefits. UHF technology excels in short-range communication scenarios, demonstrating superior obstacle penetration capabilities and reduced interference patterns. Meanwhile, VHF technology proves more effective for long-range communication needs, benefiting from enhanced groundwave propagation characteristics.
The selection between UHF and VHF frequencies requires thorough evaluation of specific operational requirements, including transmission range, signal penetration capabilities, spectrum availability, and interference conditions. Each frequency range offers distinct advantages suited to particular applications, necessitating careful assessment of these operational parameters.
Implementing the appropriate communication infrastructure ensures seamless team connectivity, facilitating efficient information flow and enhanced operational performance. Alshareef Security’s UHF and VHF two-way radio solutions enable businesses to maximize productivity while maintaining worker and customer safety standards. For expert consultation or additional information, Alshareef Security’s dedicated team stands ready to provide comprehensive support and guidance.
For more information, contact:
00966 50 7756654 00966 55 0400789